Hip Replacement
What is Hip Replacement?
Hip replacement, also known as hip arthroscopy, is a surgical operation in which a doctor removes and replaces a painful or arthritic hip joint with an artificial joint comprised of metals and plastic parts. When all other non-surgical therapy methods have failed to offer pain relief, this procedure is frequently used.
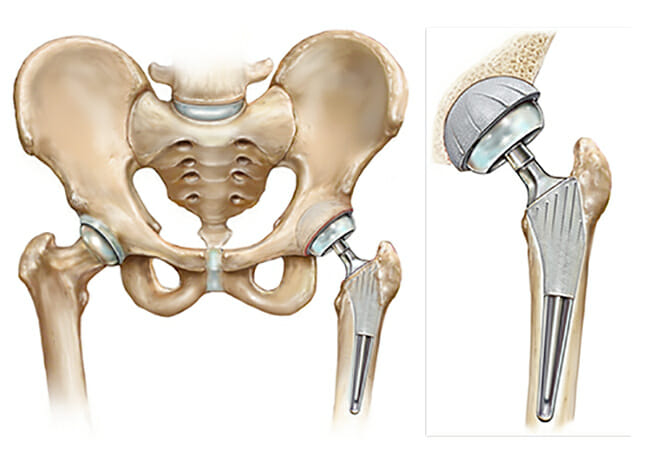
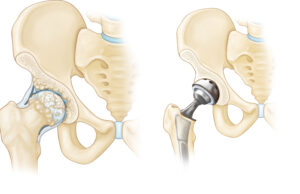
The Procedure
Pros
- Major muscular injury is reduced.
- Less post-operative discomfort Quick recovery
- Hip dislocation risk is reduced.
improved range of motion - Reduced hospital stay
Cons
- There is a possibility of nerve injury.
- There might be problems with wound healing.
Leg length variation - Certain postures may cause the implant’s ball to dislocate.
- In rare circumstances, the new implants may not be securely attached to the bone or may fall loose over time.