Digital X-Ray
Digital radiography (digital X-ray) is a form of X-ray imaging where digital X-ray sensors are used instead of traditional photographic film. Advantages include increased efficiency by eliminating the need for chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images.
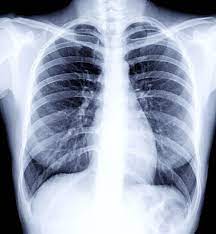
The X-ray-taking process starts with the normal X-ray source and the patient and X-ray cassette arranged in the usual positions. The difference is that the cassette contains a reusable phosphor plate which is sensitive to X-rays but not light. Once the plate has been exposed it is fed into a laser computer reader which captures the image in a digital format.
The reader then resets the plate ready for reuse. The phosphor plates are expensive but can be reused several thousand times; they are also more X-ray-sensitive than film, allowing a slightly lower radiation dose to be used. The advantages of this process over silver-film developing are the elimination of the expensive film, the absence of toxic developing chemicals and the speed. Within 30 seconds the image is visible, so if the image needs to be repeated for technical reasons this can be done immediately. If the image is satisfactory then the patient can be released thus improving the throughput of the X-ray rooms. The radiographer then orientates the image on the screen according to hospital protocols and can also alter the contrast and grey scale (a process known as windowing).


Why is a digital X-ray done
Digital X-rays, much like traditional X-rays, allow the doctor to examine inside a patient’s body. This may be useful to observe the extent of the damage done during an injury, including bone breaks and fractures. They can also detect masses in soft tissue, which could lead to the discovery of a tumour or other illnesses.
Digital X-rays are of particular interest in dentistry, where the rapid availability of the results means that a dentist can enhance the images by controlling the exposure in real time and therefore can obtain clear and detailed results that can be shared with the patient immediately. The clarity of digital X-rays makes them superior to traditional X-rays in terms of finding tiny fractures and imperfections in the teeth.
Advantages of digital X-rays
Digital X-rays have several key advantages over other options:
- Clarity – digital X-rays are capable of producing very high quality images in which the doctor or dentist can observe the scanned part of the body in very fine detail.
- Avoids the use of chemicals for developing film.
- Speed – the results are available for review immediately.
Disadvantages of digital X-rays
- The technology is expensive
- Digital X-ray technology is generally less flexible and less portable than traditional X-rays.